Characteristic of the BWR
Boiling Water Reactor (BWR) Features
Boiling water reactors (BWR) turn cooling water directly into steam within the nuclear reactor’s pressure vessel, and the steam is then used to turn the turbine generator to produce electricity.
The main feature of BWRs is that a recirculation pump decelerates the flow of water around the fuel to control the amount of bubbles (void) in the steam, which enables the output to be adjusted.
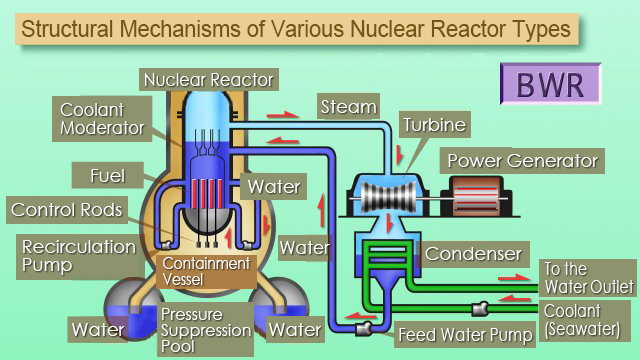
Nuclear Reactor Pressure Vessel
The fuel turns warm water into steam within this vessel. A steam separator that separates the steam from the water is located on top of the containment vessel to ensure that water does not get mixed in with the steam on its way to the turbine. Because the steam separator is located on top of the containment vessel, boiling water reactors insert the control rods from the bottom of the containment vessel with the use of water pressure.
They are also equipped with recirculation pumps and other devices, which are not found on pressurized water reactors, to control the flow of water around the fuel.
Containment Vessel
Boiling water reactor containment vessels are smaller than those on pressurized water reactors, and they are located within the nuclear reactor building. In the event of a loss of primary coolant, the steam and hot water leaving the reactor are directed from the containment vessel to a pressure suppression pool through a penetration inlet, where they are cooled and condensed to prevent a rise of pressure within the containment vessel.